How to Choose an Enterprise File Sharing Solution That Actually Works
Enterprises share 2.5 billion files per day, yet 60% of data breaches involve file sharing gone wrong. This guide breaks down what separates enterprise-grade file sharing from consumer tools, including the security features, administrative controls, and integration capabilities your IT team actually needs. This guide covers enterprise file sharing solution with practical examples.
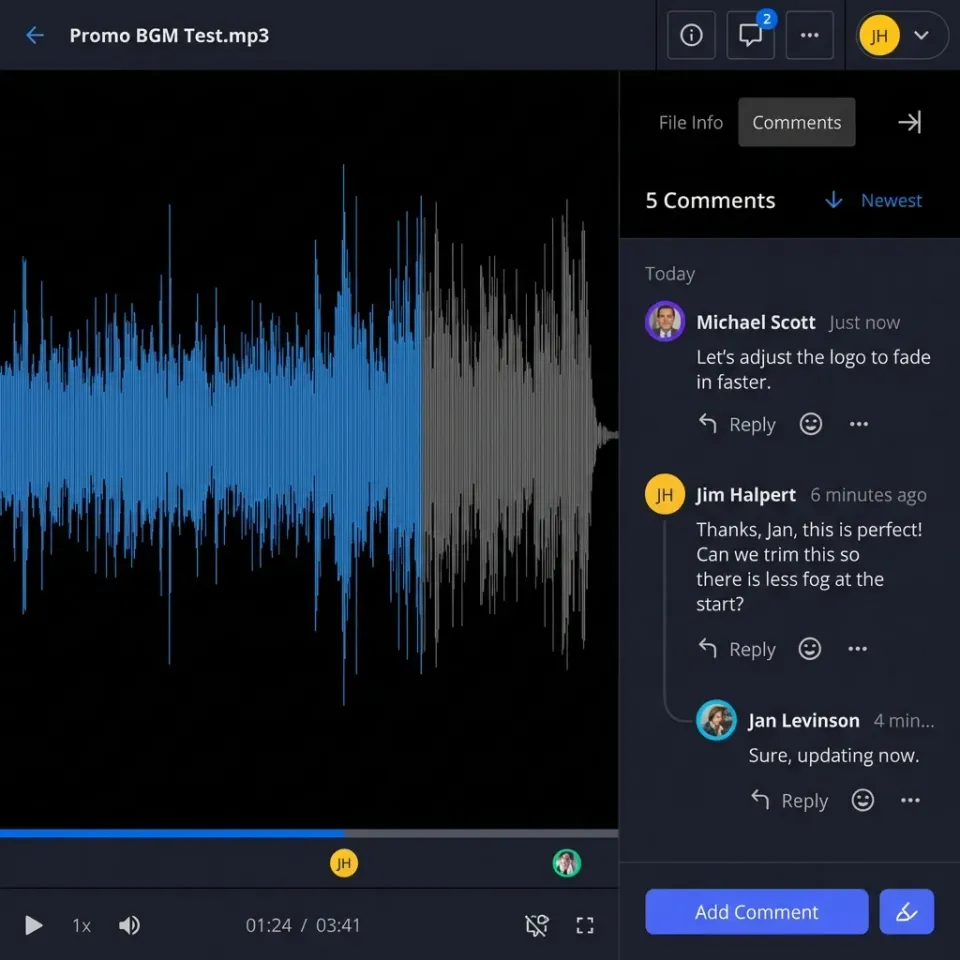
What Is an Enterprise File Sharing Solution?
An enterprise file sharing solution is a business-grade platform for sharing files internally and externally with features like access controls, audit logs, compliance support, and integration with enterprise systems. Unlike consumer tools like personal Dropbox or Google Drive accounts, enterprise solutions are built for organizational control, not individual convenience. The difference comes down to three things:
- Ownership: Files belong to the organization, not individual employees. When someone leaves, their files stay.
- Control: IT administrators can set policies, monitor activity, and revoke access across the entire organization.
- Scale: Enterprise solutions handle thousands of users, terabytes of data, and complex permission hierarchies without performance degradation. Consumer file sharing tools treat each user as an island. Enterprise solutions treat the organization as a single, manageable unit.
Helpful references: Fast.io Workspaces, Fast.io Collaboration, and Fast.io AI.
Enterprise vs. Consumer File Sharing: The Real Differences
The gap between consumer and enterprise file sharing is wider than most people realize. Here's what actually matters:
File Ownership
Consumer tools: Files live in personal accounts. When an employee leaves, you have to scramble to transfer ownership, hope they didn't delete anything, or watch critical project files walk out the door. Enterprise tools: Files belong to the organization from day one. Employee departures don't trigger data emergencies.
Administrative Control
Consumer tools: Each user manages their own sharing settings. IT has limited visibility into what's being shared with whom. Enterprise tools: Centralized admin console for setting organization-wide policies, monitoring activity, and managing user permissions at scale.
Security Features
Consumer tools: Basic password protection, maybe link expiration. That's about it. Enterprise tools: SSO/SAML integration, granular permissions (organization, workspace, folder, file level), audit logs tracking every view, download, and permission change, plus advanced link controls including domain restrictions and watermarking.
Cost Structure
Consumer tools: Per-user pricing that scales linearly. 100 users means 100x the cost. Enterprise tools: Varies. Some charge per-seat like consumer tools. Others, like Fast.io, use usage-based pricing that doesn't penalize you for adding team members.
Enterprise File Sharing Requirements Checklist
Before evaluating vendors, know what your organization actually needs. This checklist covers the features that matter for enterprise deployments:
Security Fundamentals
- Encryption at rest and in transit
- SSO/SAML integration (Okta, Azure AD, Google)
- Multi-factor authentication (MFA)
- Granular permission levels (org, workspace, folder, file)
- Complete audit logs with export capability
Sharing Controls
- Password-protected links
- Link expiration dates
- View-only mode (no download option)
- Domain restrictions (limit access to specific email domains)
- Watermarking for sensitive documents
Administrative Features
- Centralized admin console
- Organization-wide policy management
- User provisioning and deprovisioning
- Activity monitoring and reporting
- Storage and usage analytics
Collaboration Tools
- File commenting and annotations
- Version history and restore
- Real-time presence (see who's viewing)
- External guest access without requiring accounts
Integration Requirements
- Identity provider integration
- File previews for professional formats (PSD, AI, CAD, etc.)
- Large file support (no arbitrary size limits)
- API access for custom integrations
What Features Do Enterprises Actually Need?
Talk to IT teams about file sharing, and the same pain points come up again and again. Here's what actually matters:
Audit Logs That Tell the Whole Story
When something goes wrong, you need answers. Who accessed that file? When? Did they download it or just view it? Good audit logs track views, downloads, permission changes, and logins across every file, folder, and workspace. You should be able to export this data for compliance reviews or incident investigations.
Granular Permissions Without the Headache
"Everyone can access everything" doesn't work at enterprise scale. Neither does managing permissions file by file. You need a permission hierarchy: organization-wide defaults, workspace-level overrides, folder-specific rules, and file-level exceptions when necessary. The system should make the common case easy and the edge cases possible.
Guest Access That Doesn't Create Security Holes
Sharing with external partners, clients, and vendors is a reality. The question is whether you control that sharing or it happens through shadow IT. Look for solutions that let external users access specific content without requiring full accounts, and that let you revoke that access instantly when the relationship ends.
Large File Handling Without Workarounds
If your team is sharing video files, CAD drawings, or research datasets, you've probably hit file size limits. Enterprise solutions should handle large files natively, not force users to split archives or use separate transfer services.

The Hidden Cost of Per-Seat Pricing
Most enterprise file sharing vendors charge per user per month. Dropbox Business costs published pricing. Box starts at published pricing for enterprise tiers. These numbers look manageable until you do the math. A 100-person company on Dropbox Business pays published pricing, or published pricing. Add contractors, clients, and seasonal workers, and that number climbs fast. Per-seat pricing creates perverse incentives:
- IT restricts access to control costs, which pushes users to shadow IT alternatives
- Guest access becomes complicated because external users either need paid seats or workarounds
- Scaling is painful because adding headcount directly increases software costs
Usage-based pricing offers an alternative. Fast.io, for example, includes 25 seats with Pro and 100 seats with Business plans, with extra seats costing published pricing each. A 25-user team with 5TB of storage pays roughly published pricing instead of published pricing. That's a 70% reduction in cost without sacrificing enterprise features. The right pricing model depends on your organization's size and how you use file sharing. But if per-seat costs are forcing you to limit who can access files, that's a problem worth solving.
What Is the highly secure Way to Share Files in Business?
Security isn't a single feature. It's a combination of technical controls, administrative policies, and user behavior. Here's what a secure enterprise file sharing setup looks like:
Technical Controls
Encryption: Files should be encrypted at rest (stored on servers) and in transit (during upload/download). This is table stakes in 2026. SSO Integration: Single sign-on means users authenticate through your existing identity provider. No separate passwords to manage, and instant deprovisioning when someone leaves.
MFA: Multi-factor authentication adds a second layer beyond passwords. Should be enforceable organization-wide, not optional.
Access Controls
Link Restrictions: Beyond passwords and expiration dates, look for domain restrictions (only @yourcompany.com emails can access) and view-only modes that prevent downloads entirely.
Watermarking: Dynamic watermarks can embed viewer information into documents, deterring unauthorized distribution and helping trace leaks.
Revocation: The ability to revoke access instantly, even to files already shared, is critical for incident response.
Monitoring
Audit Trails: Every access, download, and share should be logged. You can't secure what you can't see.
Activity Alerts: Unusual activity, like bulk downloads or access from new locations, should trigger notifications. The highly secure approach combines all three layers: technical controls prevent unauthorized access, access controls limit what authorized users can do, and monitoring catches anomalies before they become breaches.
Evaluating Enterprise File Sharing Vendors
The market has dozens of options. Here's a framework for narrowing them down:
Start With Non-Negotiables
What does your organization require? If you need specific compliance certifications, that eliminates vendors who don't have them. If you need on-premise deployment, cloud-only vendors are out. Make a list of hard requirements before comparing features.
Compare Actual Workflows
Request a trial and test your real workflows. Upload your actual file types. Share with external partners. Check if permissions work the way you expect. Feature lists don't tell you whether the product fits how your team actually works.
Calculate Total Cost of Ownership
Per-seat pricing isn't the only cost. Factor in:
- Implementation and migration costs
- Training time for users and admins
- Integration work with existing systems
- Support and maintenance over the contract term
A cheaper per-seat price might cost more overall if implementation takes longer or adoption is slower.
Check the Roadmap
Ask vendors where their product is headed. Are they investing in features you'll need next year? How do they handle feature requests from enterprise customers? A product that fits today might not fit in three years.
Evaluate Vendor Stability
Enterprise file sharing is infrastructure. You're trusting this vendor with your organization's data. How long have they been in business? Who backs them financially? What happens to your data if they get acquired or shut down?
Frequently Asked Questions
What is an enterprise file sharing solution?
An enterprise file sharing solution is a business-grade platform for sharing files internally and externally with features like access controls, audit logs, compliance support, and integration with enterprise systems. Unlike consumer tools, enterprise solutions offer organization-level file ownership, centralized administration, and security features designed for business scale.
What is the highly secure way to share files in business?
The highly secure approach combines technical controls (encryption at rest and in transit, SSO, MFA), access controls (link restrictions, watermarking, instant revocation), and monitoring (complete audit trails, activity alerts). No single feature provides security. It's the combination of layers that protects sensitive data.
What is the difference between consumer and enterprise file sharing?
Consumer file sharing tools treat each user as independent, with personal file ownership and limited administrative control. Enterprise file sharing treats the organization as a unit, with organization-owned files, centralized policy management, granular permissions, and complete audit logging. When employees leave consumer platforms, file access becomes complicated. With enterprise solutions, files stay with the organization.
What features do enterprises need for file sharing?
Essential features include encryption, SSO/SAML integration, granular permissions at multiple levels (organization, workspace, folder, file), complete audit logs, guest access without requiring paid seats, large file support, and administrative controls for organization-wide policy management. The specific priority depends on your industry and use cases.
How much does enterprise file sharing cost?
Costs vary by vendor and pricing model. Per-seat pricing from vendors like Dropbox or Box typically runs $15-30 per user per month. Usage-based alternatives like Fast.io offer enterprise features starting at roughly published pricing for teams of 25, representing potential savings of 70% or more compared to per-seat models.
Related Resources

Start with enterprise file sharing solution on Fast.io
Fast.io gives you usage-based cloud storage built for enterprise file sharing solution. Get streaming previews, AI-powered search, and unlimited guest sharing. Start with a free account, no credit card required.